Restart times have been reduced in MySQL Cluster 6.3.28a & 7.0.9a – refer to that article for the new timings: http://www.clusterdb.com/mysql-cluster/mysql-cluster-restarts-get-faster/
Restarts are required for certain, infrequent maintenance activities. Note that there is no loss of service while a single node restarts.
When a data node restarts, it first attempts to load the data into memory from the local log files and then it will catch up with any subsequent changes by retrieveing them from the surviving node(s) in its node group.
Based on this, you would expect the time taken to restart a data node to be influenced by:
- The amount of data that was stored on the data node before the restart
- Rate of updates being made to the data during the restart
- Network performance (assuming the data is being updated during recovery)
The times will also be influenced bycertain configuration parameters, performance of the host machine and whether the multi-threaded data node (ndbmtd) is being used.
To provide some insight into how these factors impact restart times, tests have been performed where the following factors are varied:
- Database size (Each Gbyte is made up of 1,000,000 tuples in each of 5 tables)
- Whether traffic is running or not (a single thread using the NDB API to send in up to 2K tps (10K updates/second))
- Whether the 2 data nodes in the node group are on the same host or separated by a Gbit Ethernet network
The following factors are kept constant:
- Physical hosts: Intel Core 2 Quad Q8200@2.33 GHz; 7.7 GBytes RAM
- NoOfFragmentLogFiles: 300
- MaxNoOfExecutionThreads=4
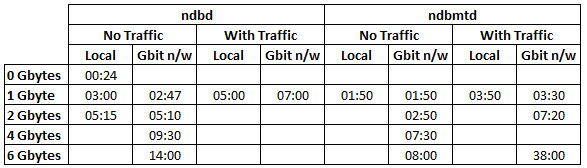
Here are the observed results:
There are a couple of things to note from these results:
- Using the multi-threaded data node (ndbmtd) greatly improves the restart time (in this case, 4 threads were available, improvements could be even greater on an 8 core/thread system)
- Results become less predictable when heavy update traffic is being processed (in this case, up to 10,000 updated rows/second on a single node group). In the tests, no attempt was made to regulate this traffic and the test application was run on the same host as the one of the data nodes. Changes to the rate of updates will vary how long it takes for the restarting node to catch-up as it’s a moving target.
There is another recovery/restart scenario. The measurements shown above assumed that the file system on the data node’s host was intact and could be used to recover the in-memory copy – if that were not the case (or the data nodes were restarted with the “initial” option) then all of the data would have to be recovered from the surviving data node(s) in the same node group. As a comparison restarting a 6 Gbyte data node with the “initial” option took 20 minutes compared to 8 minutes without it (ndbmtd, over Gbit n/w).